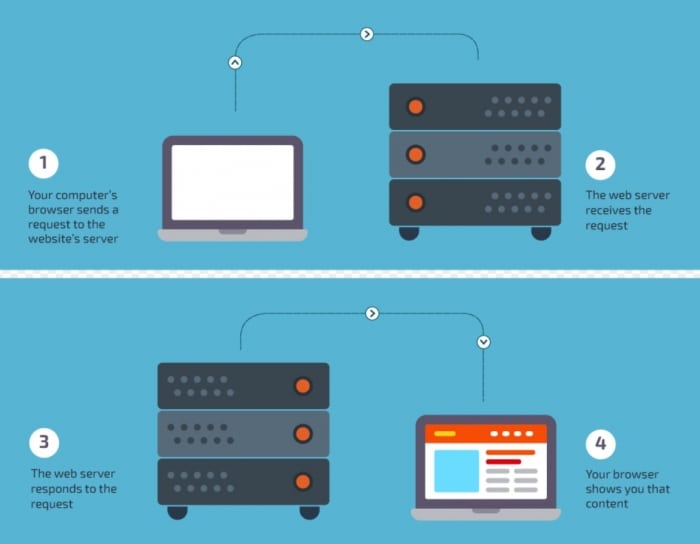
You are currently in the "Landing Pages" - Learning paths
1


Pre-Landers: Main Web Concepts Explained
5 min read
2


5 Most Common Mobile Pre-Landers That Convert
10 min read
3


How to Quickly Set Up CDN, Hosting and Domain
5 min read
4

A Guide on How to Create Converting Affiliate Landing Pages
17 min read
5

Best Ad Spy Tools for Digital Marketers
18 min read
6


AdPlexity Review: Guide + Lifetime Discount
8 min read
7


PureLander Review: Craft Affiliate Landing Pages in Just a Few Clicks
14 min read
Previous Lesson